|
|||
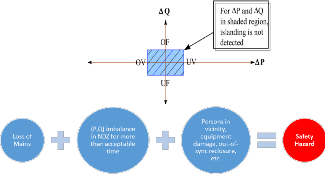 |
This project has the objective to investigate the use of LOM protection in the Cyprus electricity system. More specifically to review available LOM protection methods and standard practices used in the industry and to analyse the existing LOM methods in the Cyprus system and the issue of nuisance tripping. The final objective would be to provide suggestions to increase the reliability of the Cyprus system concerning LOM protection settings in the light of increasing penetration of distributed PV generation. |
 |
|
|
|||
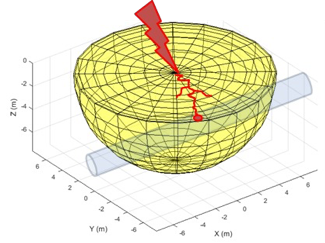 |
Wall fusion of buried pipelines can occur if the driving voltage and available current is sufficiently high. For example, it can occur from direct lightning strikes to earth, close to the pipelines’ routing. However, not all factors for defining the energy discharge needed to fuse the pipe wall are thoroughly investigated or understood. This project enriches the ongoing research activities in an attempt to understand such detrimental damages. In particular, the research is formulated around a documented wall fusion incident on an underground Gas Transmission System, due to a nearby direct lightning strike. The investigation embraces both laboratory and modelling activities to provide insights on the damaging mechanism. |
  |
|
|
|||
 |
The distribution network of Cyprus, in particular, currently uses the pro rata method of allocating losses to customers at the MV and the LV level. However, the increasing penetration of distributed energy resources (DER) is posing a challenge in terms of how the incurred losses would be affected and subsequently how they would be allocated to consumers. The objectives of this project is to develop an accurate, consistent method for the calculation of DLFs that takes into account: a)the bidirectional power flows within the distribution network and b)the underlying as well as emerging electricity market rules by addressing both the compensation as well as the charging (e.g. electricity tariffs) mechanisms. |
 |
|
|
|||
 |
This project investigates the impact of Photovoltaic oriented DC stray current corrosion on large scale solar farms’ grounding and third-party infrastructure. The DC stray current may result from a fault or facilitated by PV modules and buried cables’ condition that allows DC leakage to flow into the earth. In particular, such abnormal conditions can impact the grounding electrodes of the PV plants as well as third-party metallic infrastructures (e.g. natural gas pipelines) that are laid in the nearby vicinity of a solar plant. |
 |
|
|
|||
 |
JRC is currently providing support on the energy transition of the Republic of Cyprus with a particular emphasis in the penetration of increased amounts of Renewable Energy Sources into the power system. Towards achieving this objective, the Power System Modelling (PSM) lab is leading the following work-packages: i) Spatial and temporal modelling of the electrical demand in the Cypriot power system and ii) Identification and modelling of reference Low Voltage (LV) networks. |
 |
|
|
|||
 |
The objective is to develop smartphone applications (apple, android) that would allow field engineers to swiftly determine the type of grounding system required to achieve a specified grounding resistance. The calculation process of this application is based on formulas obtained from BS 7430:2011 Code of practice for protective earthing of electrical installations and IEEE Std 80-2000, IEEE Guide for Safety in AC Substation Grounding. |
 |
|
|
|||
 |
Many residential electricity customers have the ability to generate their own electricity using roof top PV systems. However, the generation/transmission/ distribution costs will not decrease proportionally with the decrease in the net energy requirements imposed by the PV net-metered customers. In contrast, there are increasing concerns that net energy metering policy may cause substantial cost shifts between energy customers with PV systems and other non-PV customers, particularly in the residential market. |
 |
|
|
|||
 |
Thorough evaluation of current EAC earthing practice, from generation down to distribution level. Benchmarking theoretical approaches and methodologies to practical tests and field measurements, covering aspects related to fault level calculations (as per network topologies and type of faults) and external source impedance measurements. Assist E.A.C in specific short and large scale laboratory and field testing related to the specific scope of work.
|
 |
|
|
|||
  |
A knowledge gap in transformers’ loss evaluation methods, relates to transformers which are entitled to exclusively serve large renewable plants that participate in electricity markets. The challenges arise from the fact that these transformers are obliged to serve an intermittent energy source with varying operational and financial characteristics. Thus, the key element in capitalizing the losses of such transformers is to appreciate exactly how these losses should be evaluated, bearing in mind the wind or solar resources and the ownership status of the transformer in relation to the regulatory framework of the electricity market it exists in. |
 |
|
|
|||
 |
The development of large scale photovoltaic (PV) plants in rural areas is constantly increasing. However, the knowledge of performing and installing lightning and surge protection in large scale PV plants is still premature. The main objective of this work is to provide a simulation method for assessing the external lightning protection and earthing designs that may be installed in large-scale solar applications. |
 |
|
|
|||
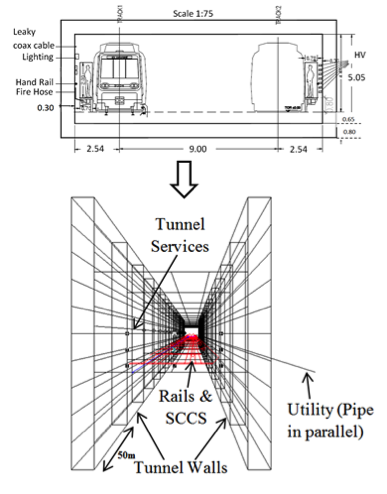 |
The tunneling construction in underground DC Metro Systems is mainly based on the Bored Tunnel Method and the Cut-and-Cover method. Therefore the stray current assessments and mitigation actions should be tailored according to which method of tunnel construction is used. The work concluded a topologically-accurate model to assess the dynamic stray current picture in cut-and-cover sections of DC metro systems. The dynamic stray current evaluation can provide an indication to the extent of the corrosion problem in the supporting and third party infrastructure of the system. |
 |
|
|
|||
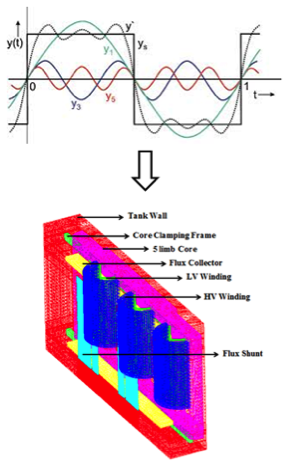 |
Most transformer finite element electromagnetic analysis is performed in the frequency domain (with an implicit sinusoidal variation of flux, current and voltage), since the calculation of the transient time domain solution, particularly of multiple cases or conditions, is currently restricted by the conventional computational power (especially in 3D). At high levels of saturation, though, core flux can be very non-sinusoidal. Where sinusoidal conditions do not hold, a time domain solution is normally indicated, however the work investigates an iterative methodology for periodic modes of sustained Ferroresonance which can be facilitated in the frequency domain. |
 |
|


